import numpy as np
import utils
import json
import pandas as pd
import utils
from scipy.stats import kendalltau
import sys
import os
import math
import random 9 Estimate \(S\) with Conjugate Priors
The basic idea of using conjugate Priors to estimate \(S\) is:
- We first estimate distribution parameters using hard K-Means, the exact procedure we covered in Section 4.1.
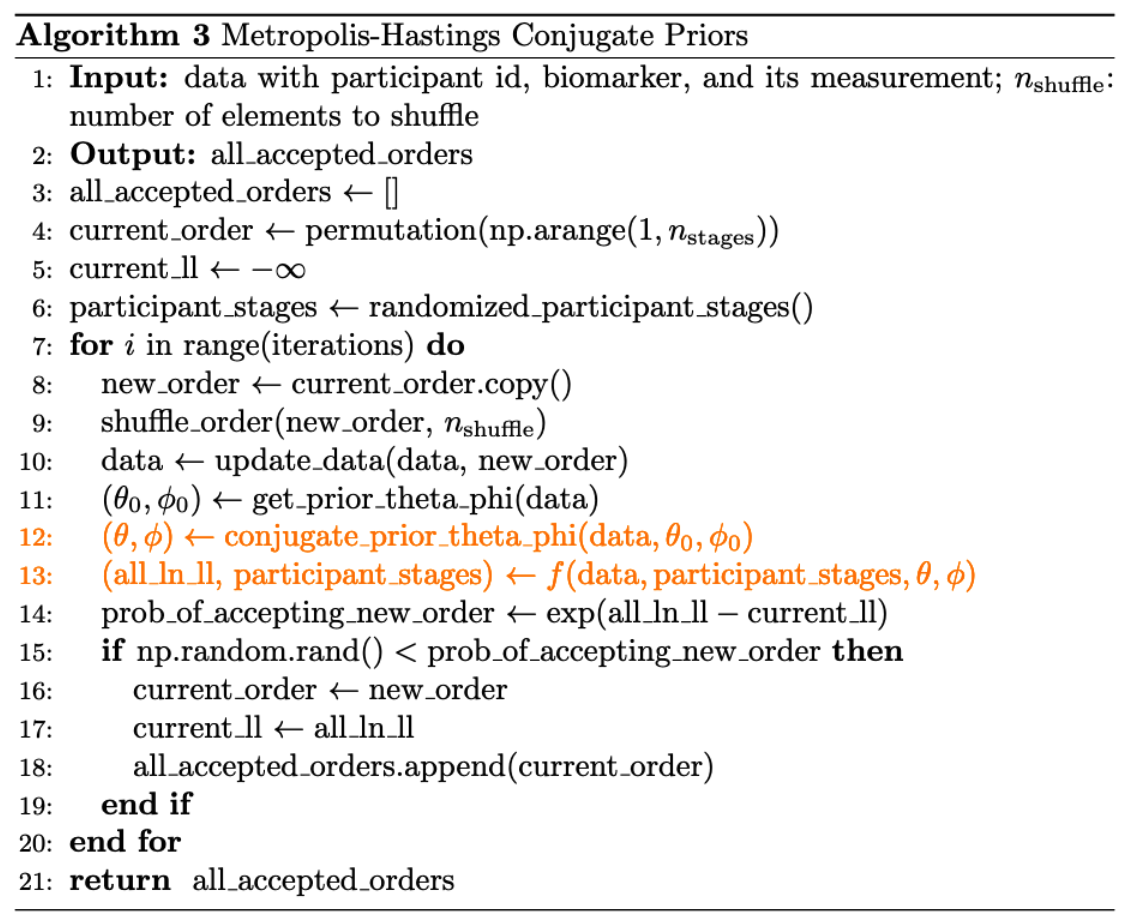
- We first randomly assign each diseased participant a stage. Then, in each iteration, we use the conjugate priors algorithm to update \(\theta, \phi\) (refer to Section 4.2) and also \(k_j\). We use Metropolis–Hastings algorithm to accept or reject a proposed \(S\).
9.1 Implementation
Code
def estimate_params_exact(m0, n0, s0_sq, v0, data):
'''This is to estimate means and vars based on conjugate priors
Inputs:
- data: a vector of measurements
- m0: prior estimate of $\mu$.
- n0: how strongly is the prior belief in $m_0$ is held.
- s0_sq: prior estimate of $\sigma^2$.
- v0: prior degress of freedome, influencing the certainty of $s_0^2$.
Outputs:
- mu estiate, std estimate
'''
# Data summary
sample_mean = np.mean(data)
sample_size = len(data)
sample_var = np.var(data, ddof=1) # ddof=1 for unbiased estimator
# Update hyperparameters for the Normal-Inverse Gamma posterior
updated_m0 = (n0 * m0 + sample_size * sample_mean) / (n0 + sample_size)
updated_n0 = n0 + sample_size
updated_v0 = v0 + sample_size
updated_s0_sq = (1 / updated_v0) * ((sample_size - 1) * sample_var + v0 * s0_sq +
(n0 * sample_size / updated_n0) * (sample_mean - m0)**2)
updated_alpha = updated_v0/2
updated_beta = updated_v0*updated_s0_sq/2
# Posterior estimates
mu_posterior_mean = updated_m0
sigma_squared_posterior_mean = updated_beta/updated_alpha
mu_estimation = mu_posterior_mean
std_estimation = np.sqrt(sigma_squared_posterior_mean)
return mu_estimation, std_estimation
def get_theta_phi_conjugate_priors(biomarkers, data_we_have, theta_phi_kmeans):
'''To get estimated parameters, returns a hashmap
Input:
- biomarkers: biomarkers
- data_we_have: participants data filled with initial or updated participant_stages
- theta_phi_kmeans: a hashmap of dicts, which are the prior theta and phi values
obtained from the initial constrained kmeans algorithm
Output:
- a hashmap of dictionaries. Key is biomarker name and value is a dictionary.
Each dictionary contains the theta and phi mean/std values for a specific biomarker.
'''
# empty list of dictionaries to store the estimates
hashmap_of_means_stds_estimate_dicts = {}
for biomarker in biomarkers:
# Initialize dictionary outside the inner loop
dic = {'biomarker': biomarker}
for affected in [True, False]:
data_full = data_we_have[(data_we_have.biomarker == biomarker) & (
data_we_have.affected == affected)]
if len(data_full) > 1:
measurements = data_full.measurement
s0_sq = np.var(measurements, ddof=1)
m0 = np.mean(measurements)
mu_estimate, std_estimate = estimate_params_exact(
m0=m0, n0=1, s0_sq=s0_sq, v0=1, data=measurements)
if affected:
dic['theta_mean'] = mu_estimate
dic['theta_std'] = std_estimate
else:
dic['phi_mean'] = mu_estimate
dic['phi_std'] = std_estimate
# If there is only one observation or not observation at all, resort to theta_phi_kmeans
# YES, IT IS POSSIBLE THAT DATA_FULL HERE IS NULL
# For example, if a biomarker indicates stage of (num_biomarkers), but all participants' stages
# are smaller than that stage; so that for all participants, this biomarker is not affected
else:
# print(theta_phi_kmeans)
if affected:
dic['theta_mean'] = theta_phi_kmeans[biomarker]['theta_mean']
dic['theta_std'] = theta_phi_kmeans[biomarker]['theta_std']
else:
dic['phi_mean'] = theta_phi_kmeans[biomarker]['phi_mean']
dic['phi_std'] = theta_phi_kmeans[biomarker]['phi_std']
# print(f"biomarker {biomarker} done!")
hashmap_of_means_stds_estimate_dicts[biomarker] = dic
return hashmap_of_means_stds_estimate_dicts
def compute_all_participant_ln_likelihood_and_update_participant_stages(
n_participants,
data,
non_diseased_participant_ids,
estimated_theta_phi,
disease_stages,
participant_stages,
):
all_participant_ln_likelihood = 0
for p in range(n_participants):
# this participant data
pdata = data[data.participant == p].reset_index(drop=True)
"""If this participant is not diseased (i.e., if we know k_j is equal to 0)
We still need to compute the likelihood of this participant seeing this sequence of biomarker data
but we do not need to estimate k_j like below
We still need to compute the likelihood because we need to add it to all_participant_ln_likelihood
"""
if p in non_diseased_participant_ids:
this_participant_likelihood = utils.compute_likelihood(
pdata, k_j=0, theta_phi=estimated_theta_phi)
this_participant_ln_likelihood = np.log(
this_participant_likelihood + 1e-10)
else:
# initiaze stage_likelihood
stage_likelihood_dict = {}
for k_j in disease_stages:
# even though data above has everything, it is filled up by random stages
# we don't like it and want to know the true k_j. All the following is to update participant_stages
participant_likelihood = utils.compute_likelihood(
pdata, k_j, estimated_theta_phi)
# update each stage likelihood for this participant
stage_likelihood_dict[k_j] = participant_likelihood
likelihood_sum = sum(stage_likelihood_dict.values())
normalized_stage_likelihood = [
l/likelihood_sum for l in stage_likelihood_dict.values()]
sampled_stage = np.random.choice(
disease_stages, p=normalized_stage_likelihood)
participant_stages[p] = sampled_stage
# use weighted average likelihood because we didn't know the exact participant stage
# all above to calculate participant_stage is only for the purpous of calculate theta_phi
this_participant_likelihood = np.mean(likelihood_sum)
this_participant_ln_likelihood = np.log(
this_participant_likelihood + 1e-10)
"""
All the codes in between are calculating this_participant_ln_likelihood.
If we already know kj=0, then
it's very simple. If kj is unknown, we need to calculate the likelihood of seeing
this sequence of biomarker
data at different stages, and get the relative likelihood before
we get a sampled stage (this is for estimating theta and phi).
Then we calculate this_participant_ln_likelihood using average likelihood.
"""
all_participant_ln_likelihood += this_participant_ln_likelihood
return all_participant_ln_likelihood
def update_data_by_the_new_participant_stages(data, participant_stages, n_participants):
'''This is to fill up data_we_have.
Basically, add two columns: k_j, affected, and modify diseased column
based on the initial or updated participant_stages
Note that we assume here we've already got S_n
Inputs:
- data_we_have
- participant_stages: np array
- participants: 0-99
'''
participant_stage_dic = dict(
zip(np.arange(0, n_participants), participant_stages))
data['k_j'] = data.apply(
lambda row: participant_stage_dic[row.participant], axis=1)
data['diseased'] = data.apply(lambda row: row.k_j > 0, axis=1)
data['affected'] = data.apply(lambda row: row.k_j >= row.S_n, axis=1)
return data
"""The version without reverting back to the max order
"""
def metropolis_hastings_with_conjugate_priors(
data_we_have,
iterations,
n_shuffle
):
n_participants = len(data_we_have.participant.unique())
biomarkers = data_we_have.biomarker.unique()
n_biomarkers = len(biomarkers)
n_stages = n_biomarkers + 1
diseased_stages = np.arange(start=1, stop=n_stages, step=1)
non_diseased_participant_ids = data_we_have.loc[
data_we_have.diseased == False].participant.unique()
# initialize empty lists
acceptance_count = 0
all_current_accepted_order_dicts = []
# initialize an ordering and likelihood
# note that it should be a random permutation of numbers 1-10
current_accepted_order = np.random.permutation(np.arange(1, n_stages))
current_accepted_order_dict = dict(zip(biomarkers, current_accepted_order))
current_accepted_likelihood = -np.inf
participant_stages = np.zeros(n_participants)
for idx in range(n_participants):
if idx not in non_diseased_participant_ids:
# 1-len(diseased_stages), inclusive on both ends
participant_stages[idx] = random.randint(1, len(diseased_stages))
for _ in range(iterations):
new_order = current_accepted_order.copy()
utils.shuffle_order(new_order, n_shuffle)
current_order_dict = dict(zip(biomarkers, new_order))
# copy the data to avoid modifying the original
data = data_we_have.copy()
data['S_n'] = data.apply(
lambda row: current_order_dict[row['biomarker']], axis=1)
# add kj and affected for the whole dataset based on participant_stages
# also modify diseased col (because it will be useful for the new theta_phi_kmeans)
data = update_data_by_the_new_participant_stages(
data, participant_stages, n_participants)
# should be inside the for loop because once the participant_stages change,
# the diseased column changes as well.
theta_phi_kmeans = utils.get_theta_phi_estimates(
data_we_have,
)
estimated_theta_phi = get_theta_phi_conjugate_priors(
biomarkers, data, theta_phi_kmeans)
all_participant_ln_likelihood = compute_all_participant_ln_likelihood_and_update_participant_stages(
n_participants,
data,
non_diseased_participant_ids,
estimated_theta_phi,
diseased_stages,
participant_stages,
)
# ratio = likelihood/best_likelihood
# because we are using np.log(likelihood) and np.log(best_likelihood)
# np.exp(a)/np.exp(b) = np.exp(a - b)
# if a > b, then np.exp(a - b) > 1
# Log-Sum-Exp Trick
max_likelihood = max(all_participant_ln_likelihood,
current_accepted_likelihood)
prob_of_accepting_new_order = np.exp(
(all_participant_ln_likelihood - max_likelihood) -
(current_accepted_likelihood - max_likelihood)
)
# it will definitly update at the first iteration
if np.random.rand() < prob_of_accepting_new_order:
acceptance_count += 1
current_accepted_order = new_order
current_accepted_likelihood = all_participant_ln_likelihood
current_accepted_order_dict = current_order_dict
acceptance_ratio = acceptance_count*100/(_+1)
all_current_accepted_order_dicts.append(current_accepted_order_dict)
# if _ >= burn_in and _ % thining == 0:
if (_+1) % 10 == 0:
formatted_string = (
f"iteration {_ + 1} done, "
f"current accepted likelihood: {current_accepted_likelihood}, "
f"current acceptance ratio is {acceptance_ratio:.2f} %, "
f"current accepted order is {current_accepted_order_dict.values()}, "
)
return all_current_accepted_order_dictsn_shuffle = 2
iterations = 10
burn_in = 2
thining = 2
base_dir = os.getcwd()
print(f"Current working directory: {base_dir}")
data_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, "data")
conjugate_priors_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'conjugate_priors')
temp_results_dir = os.path.join(conjugate_priors_dir, "temp_json_results")
img_dir = os.path.join(conjugate_priors_dir, 'img')
results_file = os.path.join(conjugate_priors_dir, "results.json")
os.makedirs(conjugate_priors_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(temp_results_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(img_dir, exist_ok=True)
print(f"Data directory: {data_dir}")
print(f"Temp results directory: {temp_results_dir}")
print(f"Image directory: {img_dir}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Read parameters from command line arguments
j = 200
r = 0.75
m = 3
print(f"Processing with j={j}, r={r}, m={m}")
combstr = f"{int(j*r)}|{j}"
heatmap_folder = img_dir
img_filename = f"{int(j*r)}-{j}_{m}"
filename = f"{combstr}_{m}"
data_file = f"{data_dir}/{filename}.csv"
data_we_have = pd.read_csv(data_file)
n_biomarkers = len(data_we_have.biomarker.unique())
if not os.path.exists(data_file):
print(f"Data file not found: {data_file}")
sys.exit(1) # Exit early if the file doesn't exist
else:
print(f"Data file found: {data_file}")
# Define the temporary result file
temp_result_file = os.path.join(temp_results_dir, f"temp_results_{j}_{r}_{m}.json")
# temp_result_file = f"{temp_results_dir}/temp_results_{j}_{r}_{m}.json"
dic = {}
if combstr not in dic:
dic[combstr] = []
accepted_order_dicts = metropolis_hastings_with_conjugate_priors(
data_we_have,
iterations,
n_shuffle,
)
utils.save_heatmap(
accepted_order_dicts,
burn_in,
thining,
folder_name=heatmap_folder,
file_name=f"{img_filename}",
title=f'heatmap of {filename}')
most_likely_order_dic = utils.obtain_most_likely_order_dic(
accepted_order_dicts, burn_in, thining)
most_likely_order = list(most_likely_order_dic.values())
tau, p_value = kendalltau(most_likely_order, range(1, n_biomarkers + 1))
dic[combstr].append(tau)
# Write the results to a unique temporary file inside the temp folder
with open(temp_result_file, "w") as file:
json.dump(dic, file, indent=4)
print(f"{filename} is done! Results written to {temp_result_file}")Current working directory: /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook
Data directory: /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook/data
Temp results directory: /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook/conjugate_priors/temp_json_results
Image directory: /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook/conjugate_priors/img
Processing with j=200, r=0.75, m=3
Data file found: /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook/data/150|200_3.csv
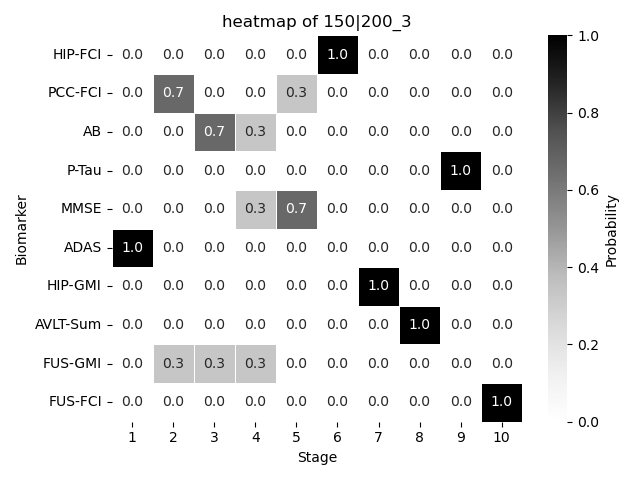
150|200_3 is done! Results written to /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook/conjugate_priors/temp_json_results/temp_results_200_0.75_3.json9.2 Result
We plot the resulting \(S\) probalistically using a heatmap.
dic{'150|200': [0.28888888888888886]}