import numpy as np
import utils
import json
import pandas as pd
import utils
from scipy.stats import kendalltau
import sys
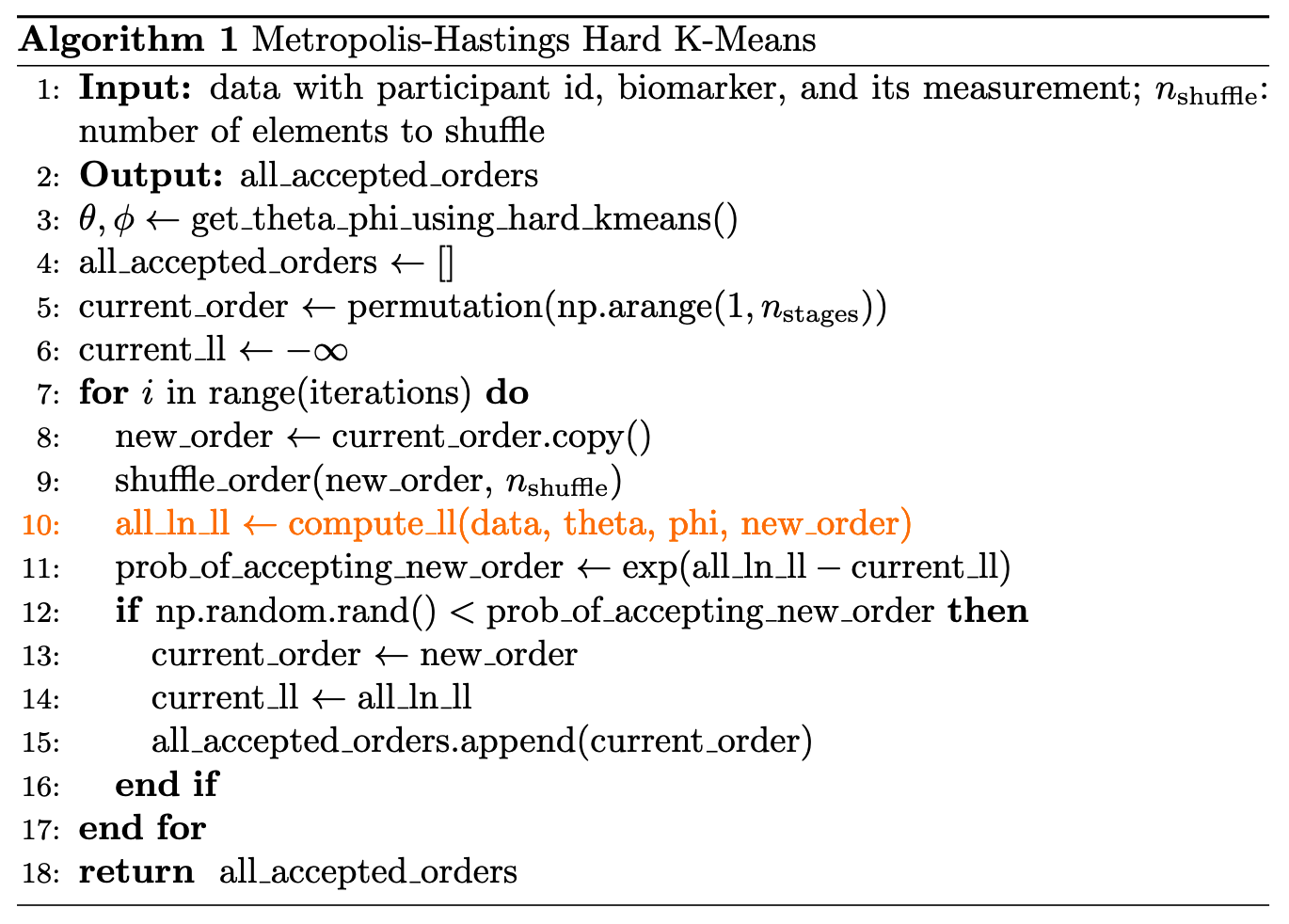
import os7 Estimate \(S\) with Hard KMeans
The basic idea of using hard K Means to estimate \(S\) is:
- We first estimate distribution parameters using hard K Means, the exact procedure we covered in Section 4.1.
- We use Metropolis–Hastings algorithm to accept or reject a proposed \(S\).
7.1 Implementation
Code
def calculate_all_participant_ln_likelihood(
iteration,
data_we_have,
current_order_dict,
n_participants,
non_diseased_participant_ids,
theta_phi_estimates,
diseased_stages,
):
data = data_we_have.copy()
data['S_n'] = data.apply(
lambda row: current_order_dict[row['biomarker']], axis=1)
all_participant_ln_likelihood = 0
for p in range(n_participants):
pdata = data[data.participant == p].reset_index(drop=True)
if p in non_diseased_participant_ids:
this_participant_likelihood = utils.compute_likelihood(
pdata, k_j=0, theta_phi=theta_phi_estimates)
this_participant_ln_likelihood = np.log(
this_participant_likelihood + 1e-10)
else:
# normalized_stage_likelihood_dict = None
# initiaze stage_likelihood
stage_likelihood_dict = {}
for k_j in diseased_stages:
kj_likelihood = utils.compute_likelihood(
pdata, k_j, theta_phi_estimates)
# update each stage likelihood for this participant
stage_likelihood_dict[k_j] = kj_likelihood
# Add a small epsilon to avoid division by zero
likelihood_sum = sum(stage_likelihood_dict.values())
# calculate weighted average
this_participant_likelihood = np.mean(likelihood_sum)
this_participant_ln_likelihood = np.log(
this_participant_likelihood + 1e-10)
all_participant_ln_likelihood += this_participant_ln_likelihood
return all_participant_ln_likelihood
def metropolis_hastings_hard_kmeans(
data_we_have,
iterations,
n_shuffle,
):
'''Implement the metropolis-hastings algorithm using simple clustering
Inputs:
- data: data_we_have
- iterations: number of iterations
- log_folder_name: the folder where log files locate
Outputs:
- best_order: a numpy array
- best_likelihood: a scalar
'''
n_participants = len(data_we_have.participant.unique())
biomarkers = data_we_have.biomarker.unique()
n_biomarkers = len(biomarkers)
n_stages = n_biomarkers + 1
non_diseased_participant_ids = data_we_have.loc[
data_we_have.diseased == False].participant.unique()
diseased_stages = np.arange(start=1, stop=n_stages, step=1)
# obtain the iniial theta and phi estimates
theta_phi_estimates = utils.get_theta_phi_estimates(
data_we_have)
# initialize empty lists
acceptance_count = 0
all_current_accepted_order_dicts = []
current_accepted_order = np.random.permutation(np.arange(1, n_stages))
current_accepted_order_dict = dict(zip(biomarkers, current_accepted_order))
current_accepted_likelihood = -np.inf
for _ in range(iterations):
# in each iteration, we have updated current_order_dict and theta_phi_estimates
new_order = current_accepted_order.copy()
utils.shuffle_order(new_order, n_shuffle)
current_order_dict = dict(zip(biomarkers, new_order))
all_participant_ln_likelihood = calculate_all_participant_ln_likelihood(
_,
data_we_have,
current_order_dict,
n_participants,
non_diseased_participant_ids,
theta_phi_estimates,
diseased_stages,
)
# Log-Sum-Exp Trick
max_likelihood = max(all_participant_ln_likelihood,
current_accepted_likelihood)
prob_of_accepting_new_order = np.exp(
(all_participant_ln_likelihood - max_likelihood) -
(current_accepted_likelihood - max_likelihood)
)
# prob_of_accepting_new_order = np.exp(
# all_participant_ln_likelihood - current_accepted_likelihood)
# np.exp(a)/np.exp(b) = np.exp(a - b)
# if a > b, then np.exp(a - b) > 1
# it will definitly update at the first iteration
if np.random.rand() < prob_of_accepting_new_order:
acceptance_count += 1
current_accepted_order = new_order
current_accepted_likelihood = all_participant_ln_likelihood
current_accepted_order_dict = current_order_dict
acceptance_ratio = acceptance_count*100/(_+1)
all_current_accepted_order_dicts.append(current_accepted_order_dict)
if (_+1) % 10 == 0:
formatted_string = (
f"iteration {_ + 1} done, "
f"current accepted likelihood: {current_accepted_likelihood}, "
f"current acceptance ratio is {acceptance_ratio:.2f} %, "
f"current accepted order is {current_accepted_order_dict.values()}, "
)
print(formatted_string)
# print("done!")
return all_current_accepted_order_dictsn_shuffle = 2
iterations = 10
burn_in = 2
thining = 2
base_dir = os.getcwd()
print(f"Current working directory: {base_dir}")
data_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, "data")
cop_kmeans_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'hard_kmeans')
temp_results_dir = os.path.join(cop_kmeans_dir, "temp_json_results")
img_dir = os.path.join(cop_kmeans_dir, 'img')
results_file = os.path.join(cop_kmeans_dir, "results.json")
os.makedirs(cop_kmeans_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(temp_results_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(img_dir, exist_ok=True)
print(f"Data directory: {data_dir}")
print(f"Temp results directory: {temp_results_dir}")
print(f"Image directory: {img_dir}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Read parameters from command line arguments
j = 200
r = 0.75
m = 3
print(f"Processing with j={j}, r={r}, m={m}")
combstr = f"{int(j*r)}|{j}"
heatmap_folder = img_dir
img_filename = f"{int(j*r)}-{j}_{m}"
filename = f"{combstr}_{m}"
data_file = f"{data_dir}/{filename}.csv"
data_we_have = pd.read_csv(data_file)
n_biomarkers = len(data_we_have.biomarker.unique())
if not os.path.exists(data_file):
print(f"Data file not found: {data_file}")
sys.exit(1) # Exit early if the file doesn't exist
else:
print(f"Data file found: {data_file}")
# Define the temporary result file
temp_result_file = os.path.join(temp_results_dir, f"temp_results_{j}_{r}_{m}.json")
dic = {}
if combstr not in dic:
dic[combstr] = []
accepted_order_dicts = metropolis_hastings_hard_kmeans(
data_we_have,
iterations,
n_shuffle,
)
utils.save_heatmap(
accepted_order_dicts,
burn_in,
thining,
folder_name=heatmap_folder,
file_name=f"{img_filename}",
title=f'heatmap of {filename}')
most_likely_order_dic = utils.obtain_most_likely_order_dic(
accepted_order_dicts, burn_in, thining)
most_likely_order = list(most_likely_order_dic.values())
tau, p_value = kendalltau(most_likely_order, range(1, n_biomarkers + 1))
dic[combstr].append(tau)
# Write the results to a unique temporary file inside the temp folder
with open(temp_result_file, "w") as file:
json.dump(dic, file, indent=4)
print(f"{filename} is done! Results written to {temp_result_file}")Current working directory: /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook
Data directory: /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook/data
Temp results directory: /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook/hard_kmeans/temp_json_results
Image directory: /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook/hard_kmeans/img
Processing with j=200, r=0.75, m=3
Data file found: /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook/data/150|200_3.csv
iteration 10 done, current accepted likelihood: -4491.553963056519, current acceptance ratio is 70.00 %, current accepted order is dict_values([1, 5, 2, 3, 9, 8, 10, 6, 4, 7]),
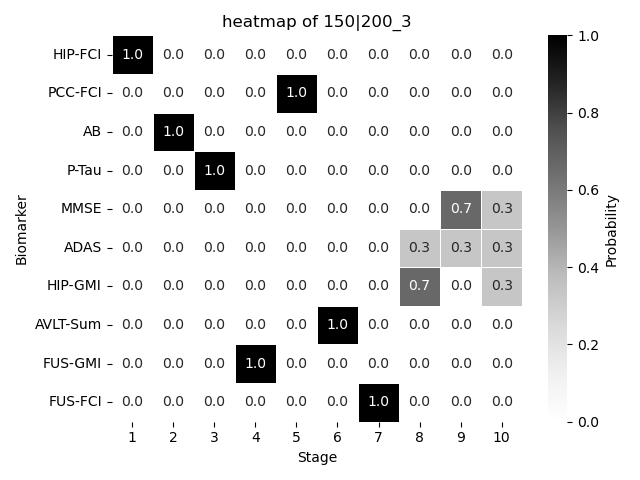
150|200_3 is done! Results written to /Users/hongtaoh/Desktop/github/ebmBook/hard_kmeans/temp_json_results/temp_results_200_0.75_3.json7.2 Result
We plot the resulting \(S\) probalistically using a heatmap. We also quantify the difference between our result with the real \(S\) using Kendall’s Tau. It ranges from \(-1\) (completely different) to \(1\) (exactly the same). \(0\) indicate complete randomness.
dic{'150|200': [0.3333333333333333]}